Urban Infrastructure in Vietnam, Current Situation and Solutions
Urban Infrastructure in Vietnam, Current Situation and Solutions
In many Smart City and Smart Urban projects, the planning phase primarily addresses issues such as announcing plans and updating new infrastructure plans. However, to ensure consistency and uniformity, the smart element must be integrated from the early stages of planning.
In recent times, the construction sector has consistently shown high growth rates, accounting for a significant portion of the country's GDP. The construction industry has contributed to economic restructuring programs, including public investment restructuring, and has played a role in the three breakthroughs in the economy, particularly in infrastructure development.
Nevertheless, the construction sector faces several challenges. Some construction plans lack vision, and the deployment is not synchronized between various planning types and levels, leading to delayed programs and projects. The supply of construction materials for projects, especially for national key projects, is sometimes insufficient and unstable. The real estate market reveals many limitations and signs of instability and is not entirely healthy.
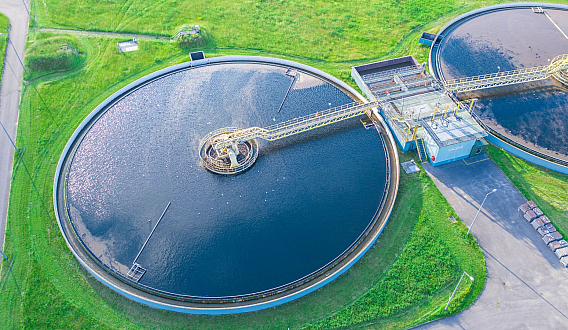
Regarding urban infrastructure, the reality in various localities indicates that the management of urban technical infrastructure development still has limitations, failing to meet the needs of residents and urban economic activities. This is especially true for transportation infrastructure, waste collection and disposal, and stormwater and wastewater treatment.
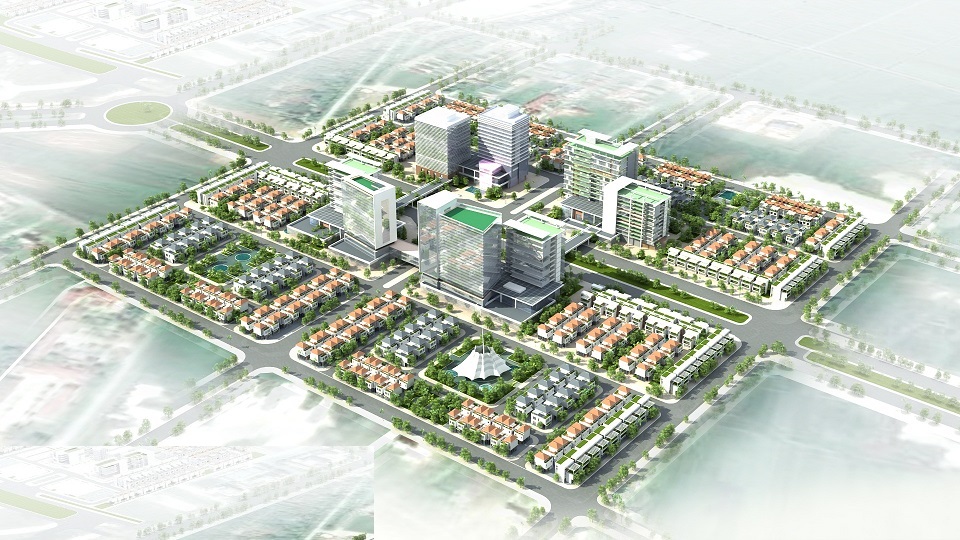

Many Solutions Needed for Urban Smartization
In Smart City planning, technical infrastructure plays a fundamental role. Designing a smart technical infrastructure system will reduce construction investment costs while increasing operational efficiency. Besides efficient design, applying information technology to collect data and automating operational coordination will significantly enhance efficiency without the need for additional construction investment.
The interconnected and coordinated operation of various infrastructure systems will also substantially increase efficiency. For example, the integration of drainage systems with underground transportation or the combination of wastewater treatment with surface drainage, recycling of solid and liquid waste for fertilizer production, or energy generation.
Smart cities, with their outstanding advantages and utilities, will gradually become a reality in future localities. However, in this process, the local government is responsible for building, providing directions, setting goals, and developing solutions for smart urban projects.